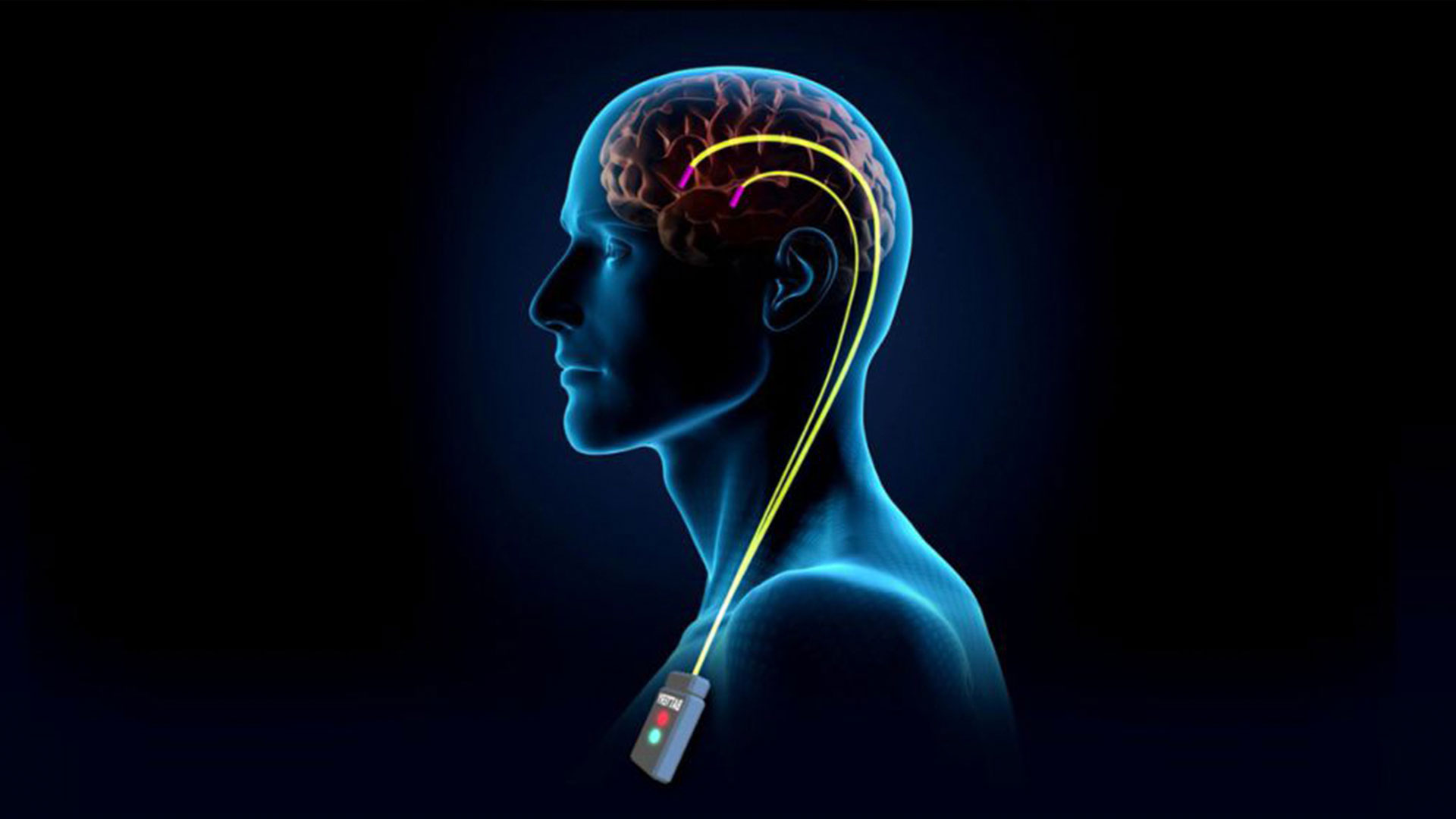
What is a Brain Battery?
People can lose their mobility and control if there is an injury to the brain areas that contain specialized cells involved in brain cell movement control, or if there is insufficient synthesis of substances known as neurotransmitters responsible for maintaining this control. These two problems can contribute to loss of both movement and control.
The primary surgical method used in the treatment of neurological diseases that cause these disorders is the brain pacemaker. Multiple sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease are examples of these diseases. People suffering from essential tremor (uncontrolled shaking during voluntary movements), Parkinson’s disease, and dystonia have benefited significantly from brain batteries (involuntary contraction), one of the surgical treatments that can be modified and controlled.
Neurosurgical procedures performed using modern technologies are less risky than other neurosurgery procedures. The disease can be controlled by adjusting the patient’s complaints. Electrodes placed on the patient can be replaced without touching the patient, thanks to the brain battery. Patients who have undergone a brain pacing procedure, particularly those with Parkinson’s, can experience an improvement in their quality of life and resume their regular lifestyle as before the procedure.
What are the Effects of the Brain Battery?
Patients who have undergone brain pacing operation can return to their daily lives quickly. The severity of a person’s symptoms can significantly affect a person’s daily activities, especially in people with Parkinson’s disease who experience involuntary contractions. Patients who cannot control their movements do so for a variety of reasons, including tremors and excessive muscle contraction.
As a result of brain batteries, patients suffering from these symptoms can revert to the earliest stages of their illness. Patients who have undergone a brain pacing procedure often observe a reduction in their medication dosage, although some of these individuals may discontinue their prescriptions. Although this battery effectively treats the symptoms, it is not a cure for the disease.
Most neurological disorders are caused by trauma to specific brain areas. The brain battery does not return damaged parts to their normal state. Still, it can help reduce symptoms caused by a failure in this area, such as tremors, inability to control movement, and slowing of the patient’s movements.
The battery relieves these symptoms, which is beneficial for Parkinson’s patients. Patients with advanced Parkinson’s disease in their tenth year of life who have undergone pacing surgery have the potential to regress to the early stages of the disease. Patients who cannot do their daily work such as buttoning their shirt, cooking, tying their shoes and who are isolated from social life can continue their daily lives without the need for help.
How is Brain Battery Surgery Performed?
These applications aim to provide regular electrical stimulation to the brain to restore normal function to damaged or impaired electrical activity. In order to achieve this goal, it is necessary to first map the brain of the patients. In addition to other imaging techniques, MRI was used to create the map.
Then, using this map as a guide, the locations of the electrodes are determined and thin wires are placed at these locations so that the electrodes can generate electrical activity. The battery to provide electrical stimulation will be implanted under the collarbone or in the cavity of the rib cage. Although this surgery is performed in this primary method, various surgeries are performed before, during and after.
Before Surgery
Various diagnostic procedures are performed on patients, including tests and examinations, prior to surgery to determine their overall health. Imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computerized tomography (CT) of the brain are used in the extraction of patient brain maps.
In addition, patients undergo a series of tests to assess their suitability for sedation. Blood and urine tests are done to get a general idea of the patient’s condition. Checks showing the general health status such as blood count, hormone level and kidney activity are completed. In this way, it is possible to determine whether the patients are ready for surgery.
In addition to these tests, doctors will also perform other tests they deem necessary. As a result of these operations, patients experience physical and psychological effects. Doctors will sometimes ask their patients to attend psychiatric consultations to get some relief from their difficulties. After all these tests and examinations, listening to the patient’s medical history and learning the medications he is taking, the patient is now ready for surgery.